
|
|
|
|
|
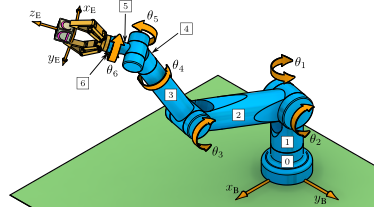
Example 5.02:: Helical Pair: Screw Coordinates (MATLAB)
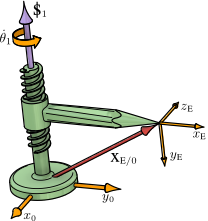
This example illustrates how to determine a helical pair's joint-rate, screw coordinates, and pitch from its Cartesian twist 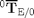 .
.
Contents
Clear All Workspace Objects and Reset All Assumptions
%clear all
The Cartesian twist 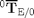
TwistERel0Res0 = [0; 0; 2; -40; 0; 10] % [rad/s; cm/s]
TwistERel0Res0 =
0
0
2
-40
0
10
a) The Joint-Rate 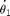
omegaERel0Res0 = [TwistERel0Res0(1); TwistERel0Res0(2); TwistERel0Res0(3)]; % [rad/s] VERel0Res0 = [TwistERel0Res0(4); TwistERel0Res0(5); TwistERel0Res0(6)]; % [cm/s] theta1Dot = norm(omegaERel0Res0) % rad/s
theta1Dot =
2
b) Screw Coordinates ![$^{0}\hspace{0.34em}\rule[-0.17em]{0.01in}{1.0em}\hspace{-0.34em}{\mathbf S}_{1|\mathrm E}$](Example05_02_eq93722.png)
S1Res0 = omegaERel0Res0/theta1Dot %[unitless] SO1ERes0 = VERel0Res0/theta1Dot % [cm] Screw1ERes0 = [S1Res0; SO1ERes0] % [unitless; cm]
S1Res0 =
0
0
1
SO1ERes0 =
-20
0
5
Screw1ERes0 =
0
0
1
-20
0
5
c) Pitch 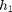
h1 = dot(S1Res0, SO1ERes0) % cm
h1 =
5
This MATLAB example illustrates a computation from the textbook Fundamentals of Robot Mechanics by G. L. Long, Quintus-Hyperion Press, 2015. See http://www.RobotMechanicsControl.info for additional relevant files.